Definition
Interface that can read any class in the collection framework.
Thus, we can read arraylist or linkedlist or hashmap with iterator.
why we use iterator?
Since we can read any list or set with iterator, we do not have to fix or change code when you work with big projects.
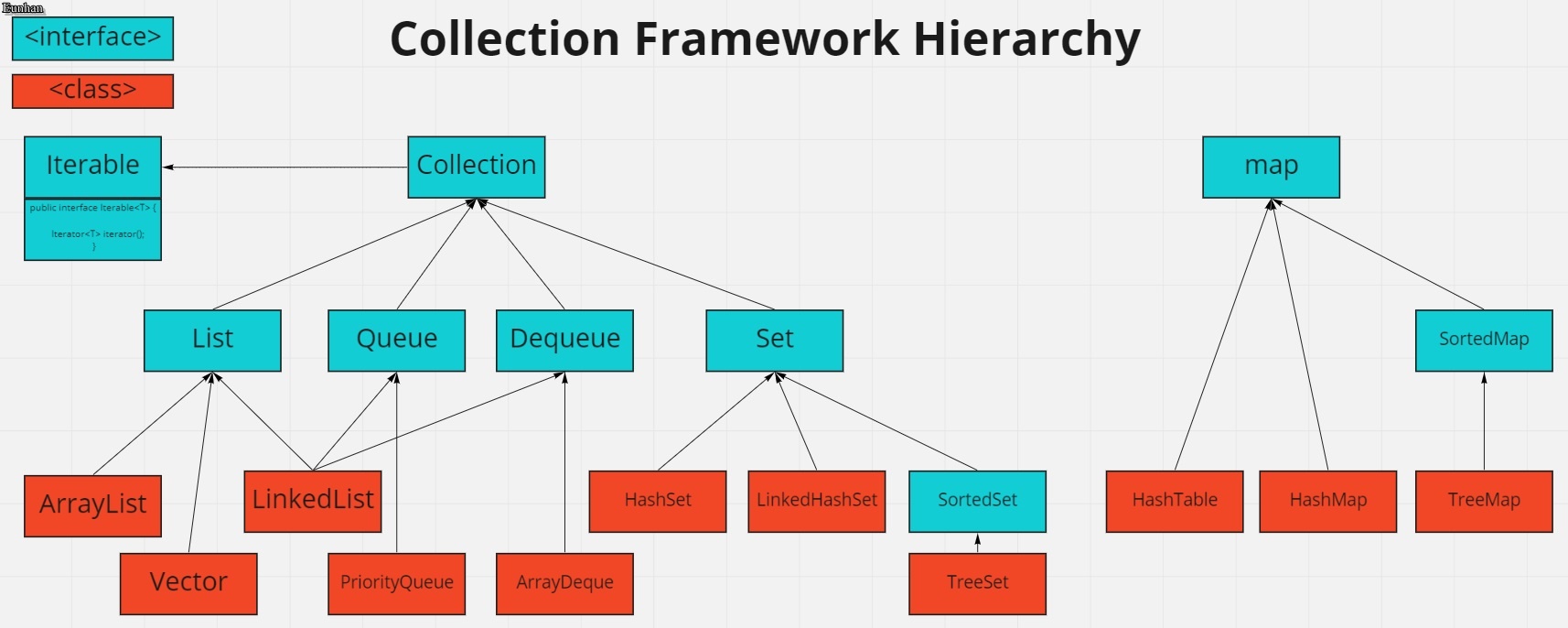
Hierarchy
method
hasNext() next() remove()
method Example
List list = new ArrayList();// arrayList
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
Iterator <string> itr = list.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
String str = itr.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
iterator Example
@Test
public void multipleIterators() {
final Iterator<Integer> a = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).iterator();
final Iterator<Integer> b = Arrays.asList(6).iterator();
final Iterator<Integer> c = new ArrayList<Integer>().iterator();
final Iterator<Integer> d = new ArrayList<Integer>().iterator();
final Iterator<Integer> e = Arrays.asList(7, 8, 9).iterator();
final Iterator<Integer> singleIterator = Iterators.singleIterator(Arrays.asList(a, b, c, d, e));
assertTrue(singleIterator.hasNext());
for (Integer i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
assertEquals(i, singleIterator.next());
}
assertFalse(singleIterator.hasNext());
}